As the sun rises over China’s bustling tech hubs, a revolution is quietly unfolding beneath the surface. The nation’s meteoric rise in artificial intelligence (AI) development is not just reshaping industries; it is also redefining the very nature of information dissemination and control. While advancements in AI promise unparalleled efficiency and innovation, they also bring with them a pair of significant censorship dilemmas. As algorithms become more sophisticated, so too does the potential for manipulation, raising critical questions about freedom of expression and governmental oversight. In this article, we delve into the complexities of China’s AI boom, exploring the dual-edged implications it poses for censorship in the digital age.
Table of Contents
- Chinas Explosive AI Growth and the Challenges of Information Control
- Navigating the Fine Line: Innovation vs. Censorship in Chinas AI Landscape
- Implications for Global Discourse: The Ripple Effect of Chinas AI Policies
- Strategic Recommendations for Balancing Progress and Ethical Standards in AI Development
- Q&A
- Final Thoughts
Chinas Explosive AI Growth and the Challenges of Information Control
As China accelerates its AI advancements, the tightrope between innovation and information control becomes increasingly perilous. The nation’s government has embraced AI technologies to enhance economic productivity and industry competitiveness; however, this rapid growth raises significant concerns about content censorship and surveillance. Algorithms developed in this environment are not only meant to streamline everyday tasks but also to scrutinize and manage the digital landscape, posing potential threats to individual freedoms and public discourse.
To shed light on these issues, two major red flags stand out:
- Content Manipulation: The state’s investment in AI-driven systems enables the monitoring and filtering of information, often leading to the suppression of dissenting viewpoints. This creates an environment where public opinion can be artificially shaped by controlling access to the truth.
- Impaired Innovation Ecosystem: While innovation thrives in an open environment, excessive information control discourages creative thought. When developers fear repercussions for exploring controversial ideas, the overall growth of the AI field may stagnate, ultimately hampering China’s global competitiveness.
| Aspect | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Public Discourse | Limited representation of diverse opinions |
| Innovation | Stifled ideas due to fear of reprisals |

Navigating the Fine Line: Innovation vs. Censorship in Chinas AI Landscape
The dynamic landscape of artificial intelligence in China is marked by rapid advancements, yet it simultaneously raises pressing concerns regarding censorship. As innovative applications leverage vast amounts of data to enhance user experiences and improve efficiencies, the need for oversight becomes paramount. The government’s control over information can stifle creativity and limit the potential of AI technologies. Key issues include:
- Data Privacy: The fine line between innovation and the invasive potential of surveillance tools can jeopardize individual freedoms.
- Manipulation of Information: AI systems may propagate state-approved narratives, suppressing dissenting voices and skewing public perception.
As AI systems become more integral to daily life, distinguishing genuine innovation from state-controlled narratives becomes increasingly challenging. The interplay between a burgeoning tech sector and stringent regulatory frameworks creates a paradox where innovation flourishes, yet the scope for creative expression diminishes. To illustrate the current state of affairs, consider the following table that highlights key areas of tension:
| Aspect | Innovation Potential | Censorship Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Content Creation | Enhanced storytelling through AI-generated media | Repression of non-conforming narratives |
| Consumer Data Analytics | Personalized experiences and improved services | Exploitation of user data for surveillance |
| Social Media Algorithms | Optimized engagement through targeted content | Promotion of propaganda over free discourse |
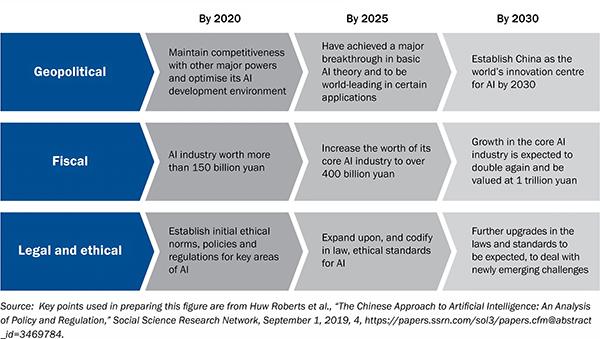
Implications for Global Discourse: The Ripple Effect of Chinas AI Policies
The rapid expansion of China’s AI capabilities not only influences its domestic landscape but also reverberates across global discourse in profound ways. As Chinese censorship policy intertwines with the nation’s AI advancements, countries worldwide may find themselves reassessing their own approaches to digital governance and information control. This dual-edged sword has the potential to lead to a domino effect, as other nations might adopt similar stances towards AI, particularly in terms of manipulation and surveillance. Key considerations include:
- Standardization of Censorship: The push for uniform AI regulations may inadvertently encourage a unified global approach to content moderation, often at the cost of freedom of expression.
- Increased Digital Authoritarianism: As governments worldwide observe China’s model, they may be inspired to reinforce state control over information dissemination under the guise of security.
Furthermore, international collaboration on AI policy may become contentious as trust issues surface, particularly regarding data sharing and ethical standards. Countries wary of China’s intentions could leverage AI as both a tool and a weapon in geopolitical strategies. This emerging landscape could lead to a polarized technological environment, characterized by:
| Aspect | Potential Outcome |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Divergence | Inconsistent AI policies can stifle international cooperation. |
| AI as a New Battlefield | Increased competition and conflict over AI supremacy. |

Strategic Recommendations for Balancing Progress and Ethical Standards in AI Development
To navigate the intricate landscape of AI development, it is crucial to adopt a balanced approach that fosters innovation while upholding ethical standards. One of the primary strategies is to establish multistakeholder frameworks that include governments, tech companies, civil society, and academia. These frameworks can ensure diverse perspectives are integrated into the decision-making process. Key actions could include:
- Creating clear regulatory guidelines that promote transparency.
- Encouraging collaboration among AI developers to share best practices.
- Implementing ethical training programs for AI practitioners.
Moreover, the deployment of auditable AI systems can significantly reduce the risk of censorship and ethical violations. This involves incorporating machine learning models that are both interpretable and adaptable, allowing for regular assessments of their impact on society. To facilitate this, organizations might consider the following:
| Action | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Regular AI Impact Assessments | Identify potential biases and mitigate risks. |
| Public Engagement Initiatives | Increase awareness and public trust in AI technologies. |
Q&A
Q&A: China’s AI Boom Raises 2 Massive Censorship Red Flags
Q1: What is the current state of AI development in China?
A1: China is experiencing a rapid and expansive AI boom, driven by substantial government investment, a thriving tech industry, and a vast amount of data from its population. Companies are developing cutting-edge technology in areas such as facial recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous systems. This growth positions China as a global leader in AI innovation, with an aim to integrate AI into various sectors, including healthcare, transportation, and urban management.
Q2: What are the two major censorship red flags discussed in relation to China’s AI boom?
A2: The two major censorship red flags involve the potential for AI to enhance the capacity for surveillance and the use of algorithms to manipulate information. Firstly, the advanced technologies being developed can bolster the government’s ability to monitor its citizens more effectively, leading to concerns about privacy and personal freedoms. Secondly, algorithms could be employed to filter and control the information accessible to the public, stifling freedom of expression and critical discourse.
Q3: How does AI technology contribute to surveillance in China?
A3: AI technology, particularly facial recognition and data analytics, can significantly enhance the surveillance capabilities of the state. With an extensive network of cameras and monitoring systems, AI can track individuals in real-time, identify patterns of movement, and predict behavior. This level of scrutiny raises concerns over the infringement of civil liberties and the potential for abuses of power by the authorities.
Q4: Can you elaborate on how content manipulation through algorithms poses a red flag?
A4: Content manipulation through algorithms refers to the sophisticated use of AI to curate and control the types of information that are available to citizens. In China, state-sponsored platforms may employ these algorithms to promote certain narratives while suppressing dissenting opinions. This not only affects public perception but also limits the diversity of information, undermining informed citizenship and democratic discourse.
Q5: What implications do these red flags have for global engagement with Chinese AI companies?
A5: The implications are profound, as countries and corporations face the dilemma of engaging with China’s burgeoning AI industry while grappling with the ethical and moral ramifications of potential complicity in censorship and surveillance. Internally, nations may reassess partnerships based on the need to uphold human rights and freedom of expression. Externally, this may lead to a divide in tech alliances, as democratic nations seek to establish frameworks to curb the risks associated with Chinese AI technologies.
Q6: What can be done to address these censorship concerns?
A6: Addressing these concerns may involve implementing transparent policies and open standards for AI development that include ethical considerations, stakeholder engagement, and independent oversight. By fostering international dialog and cooperation, especially between countries with differing governance models, it may be possible to establish norms and safeguards that prevent the misuse of AI technologies for censorship and surveillance.
Q7: Where does the AI race leave the rest of the world?
A7: The swift advancement of AI in China compels other nations to accelerate their own AI initiatives, not just for technological competitiveness but also to safeguard their democratic values. As a result, there could be a global push for establishing ethical guidelines in AI deployment, ensuring that technological progress does not come at the cost of personal freedoms and social justice. The race is not merely about innovation but also about defining the future of human rights in an increasingly digital world.
Final Thoughts
China’s rapid ascent in the realm of artificial intelligence serves as a double-edged sword, illuminating both the remarkable technological advancements and the concerning implications tied to censorship. As the nation positions itself at the forefront of AI innovation, the tightrope between progress and free expression grows increasingly precarious. The two significant red flags raised by this boom—government control over information and the potential for AI-driven surveillance—serve as critical reminders of the ethical considerations that must accompany technological growth.
Moving forward, it is imperative for global observers to engage in a nuanced dialog about the balance of innovation and human rights. The choices made today will undoubtedly shape the future landscape not just of China’s AI ecosystem, but also of global norms surrounding technology, autonomy, and the flow of information. As we navigate this intricate terrain, let us hope for a future where advancements do not come at the expense of fundamental freedoms, but rather complement the ideals of openness and shared knowledge. The story of China’s AI boom is just beginning; its next chapters will undoubtedly challenge us to think critically about the power of technology in our interconnected world.

ivermectin 12 mg tablets for humans – stromectol pills canada order generic carbamazepine 400mg
isotretinoin 20mg pills – purchase zyvox pills cheap linezolid
oral amoxil – buy amoxicillin paypal combivent pills
buy generic azithromycin for sale – how to get tindamax without a prescription bystolic 20mg without prescription
prednisolone medication – brand azithromycin progesterone 200mg drug
order neurontin 100mg for sale – purchase anafranil pills sporanox for sale online
buy lasix generic diuretic – buy furosemide 100mg for sale betnovate 20gm cheap
cost monodox – order glucotrol for sale glipizide usa
order augmentin 1000mg – order ketoconazole online order cymbalta pill
augmentin 1000mg price – purchase augmentin pill duloxetine without prescription
buy semaglutide 14 mg pills – buy vardenafil 20mg generic buy periactin 4 mg pills
where can i buy zanaflex – order hydrochlorothiazide generic buy generic hydrochlorothiazide 25mg
generic tadalafil 10mg – us pharmacy cialis buy sildenafil 50mg for sale
viagra us – cialis overnight shipping order tadalafil 20mg sale
cenforce 100mg canada – chloroquine 250mg canada purchase glycomet generic
buy atorvastatin 10mg online cheap – amlodipine cost lisinopril buy online
prilosec cost – order prilosec 10mg generic order atenolol pill
buy depo-medrol medication – buy pregabalin 150mg online cheap how to buy aristocort
brand desloratadine – buy desloratadine 5mg for sale buy priligy generic
oral cytotec – misoprostol us buy diltiazem paypal
zovirax cheap – cheap crestor cost crestor 20mg
purchase domperidone without prescription – buy sumycin 500mg online buy cheap generic cyclobenzaprine
how to get motilium without a prescription – purchase flexeril online cheap flexeril without prescription
purchase inderal – inderal online order methotrexate for sale
coumadin 5mg for sale – losartan order online cozaar 25mg us
order generic esomeprazole 20mg – buy nexium for sale imitrex 25mg without prescription
buy levofloxacin 500mg for sale – order ranitidine ranitidine 150mg without prescription
mobic pills – celebrex 100mg generic order generic flomax 0.4mg
ondansetron 8mg canada – zofran 8mg for sale order zocor 20mg generic
buy valacyclovir 1000mg generic – buy valtrex 500mg pill forcan pill
I’ll certainly return to read more.
buy provigil 200mg pill purchase modafinil generic provigil 100mg price purchase modafinil sale provigil 100mg brand buy provigil 100mg online cost modafinil
This is the amicable of glad I take advantage of reading.
This is a theme which is virtually to my verve… Numberless thanks! Faithfully where can I lay one’s hands on the phone details due to the fact that questions?
buy cheap azithromycin – buy tindamax 500mg online buy flagyl without a prescription
rybelsus 14mg price – order periactin 4mg pill cheap cyproheptadine
motilium medication – order domperidone 10mg online buy cyclobenzaprine for sale
inderal sale – methotrexate drug buy methotrexate generic
amoxil pills – order amoxil without prescription buy combivent for sale
buy zithromax 250mg – order tindamax 500mg online cheap brand bystolic 20mg
buy augmentin online – https://atbioinfo.com/ order ampicillin without prescription
buy generic nexium over the counter – nexium to us buy nexium capsules
buy coumadin 5mg – https://coumamide.com/ cost hyzaar
buy meloxicam pill – mobo sin buy mobic without prescription
buy prednisone 5mg online cheap – https://apreplson.com/ purchase prednisone pill
buy generic ed pills online – medication for ed dysfunction best drug for ed
oral amoxicillin – https://combamoxi.com/ buy amoxil pills
buy diflucan 100mg generic – generic diflucan 200mg buy generic diflucan over the counter
cenforce uk – https://cenforcers.com/# cenforce 50mg over the counter
online cialis no prescription – cialis sales in victoria canada cialis medicine
ranitidine online order – ranitidine tablet how to get ranitidine without a prescription
cialis australia online shopping – https://strongtadafl.com/ how much does cialis cost at walgreens
Greetings! Jolly useful recommendation within this article! It’s the crumb changes which liking turn the largest changes. Thanks a quantity for sharing! lasix 20 mg para que sirve
sildenafil oral jelly 100mg kamagra – https://strongvpls.com/# 50 mg generic viagra
Thanks on putting this up. It’s understandably done. order azithromycin 500mg for sale
I am in fact happy to gleam at this blog posts which consists of tons of of use facts, thanks representing providing such data. https://ursxdol.com/clomid-for-sale-50-mg/
This website exceedingly has all of the tidings and facts I needed there this case and didn’t identify who to ask. https://prohnrg.com/product/orlistat-pills-di/
More delight pieces like this would create the интернет better. ordonnance pour cialis
This is the big-hearted of scribble literary works I truly appreciate. https://ondactone.com/product/domperidone/
Thanks for sharing. It’s first quality.
https://proisotrepl.com/product/domperidone/
This is the stripe of glad I enjoy reading. http://www.cs-tygrysek.ugu.pl/member.php?action=profile&uid=98491
order forxiga 10 mg pills – https://janozin.com/# buy generic forxiga online
order orlistat pills – janozin.com buy orlistat tablets
Thanks on putting this up. It’s understandably done. https://sportavesti.ru/forums/users/huyvv-2/
You can protect yourself and your dearest by being cautious when buying medicine online. Some pharmaceutics websites function legally and put forward convenience, secretiveness, rate savings and safeguards as a replacement for purchasing medicines. buy in TerbinaPharmacy https://terbinafines.com/product/lamisil.html lamisil
Greetings! Utter gainful par‘nesis within this article! It’s the crumb changes which choice obtain the largest changes. Thanks a portion for sharing! TerbinaPharmacy
This is the tolerant of delivery I unearth helpful.
https://t.me/s/ef_beef
https://t.me/s/Top_BestCasino/173
https://t.me/officials_pokerdom/3400
https://t.me/s/RejtingTopKazino
https://t.me/s/iGaming_live/4868
https://t.me/s/bEEfCaSiNo_OffiCIALs
https://t.me/s/beEfCASiNO_OffICiAlS
В джунглях игр, где каждый площадка норовит привлечь заверениями простых выигрышей, рейтинг топ онлайн казино
превращается именно той ориентиром, что проводит через заросли рисков. Игрокам профи и начинающих, которые пресытился от ложных обещаний, это помощник, чтоб увидеть настоящую выплату, как ощущение выигрышной фишки у пальцах. Без ненужной болтовни, только проверенные сайты, где выигрыш не просто число, но ощутимая фортуна.Собрано по гугловых поисков, будто сеть, что захватывает топовые горячие тренды по интернете. В нём минуя места про стандартных фишек, каждый элемент словно ставка в покере, там обман выявляется мгновенно. Профи понимают: на стране стиль речи с иронией, где юмор скрывается под рекомендацию, даёт обойти обмана.В http://www.don8play.ru/ этот топ находится как готовая карта, подготовленный к старту. Посмотри, коли нужно увидеть пульс реальной азарта, обходя иллюзий да провалов. Для кто ценит вес выигрыша, такое будто взять фишки на ладонях, вместо глядеть по монитор.