In the grand tapestry of global economics, few threads weave as intricate a pattern as that of Russia’s economy. Often cloaked in bravado, the narrative of a powerful and formidable economic force has captivated policymakers, analysts, and the curious public alike. However, beneath the surface glimmer of impressive statistics and an ambitious industrial façade, a deeper examination reveals a more complex picture. This article delves into the nuances of Russia’s economic landscape, challenging the perception of strength that has so often dominated discussions. By peeling back the layers, we aim to uncover the underlying fragilities and structural challenges that may suggest Russia’s economy was never as robust as it appeared. Join us as we explore the realities that have shaped this enigmatic powerhouse and consider the implications for both Russia and the broader global stage.
Table of Contents
- The Mirage of Economic Strength: Unpacking Russias Growth Statistics
- Structural Weaknesses: The Hidden Flaws in Russias Economic Model
- Geopolitical Pressures: How Sanctions Expose Vulnerabilities
- Path to Resilience: Strategic Recommendations for Future Economic Stability
- Q&A
- Key Takeaways

The Mirage of Economic Strength: Unpacking Russias Growth Statistics
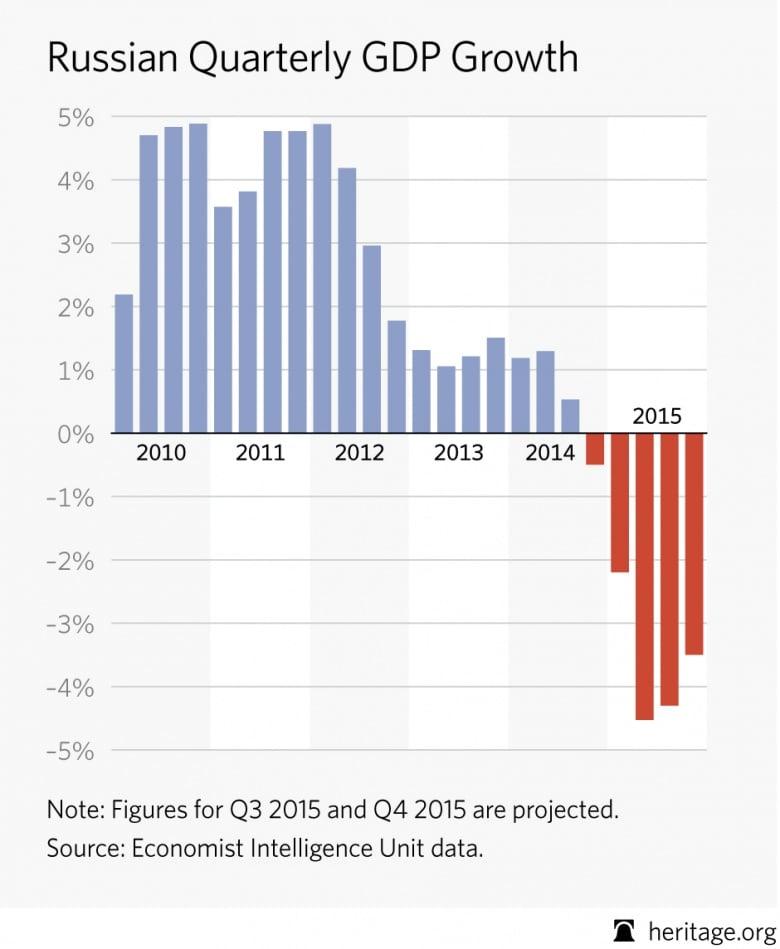
The perception of Russia’s economic prowess has often been embellished by tailored statistics that paint a rosier picture than reality. For years, foreign investments and trade surpluses contributed to a narrative of strength, but a closer look reveals underlying vulnerabilities. Factors such as flawed data representation, manipulative government policies, and external pressures have created an illusion of stability. The critical dependencies on commodities and energy exports leave the economy exposed to market volatility, raising questions regarding the sustainability of reported growth rates.
Furthermore, the concentration of wealth within a small elite raises alarms about the true health of the economy. Consider the following points:
- Inflation and cost of living: Consistently high inflation undermines real purchasing power.
- Currency fluctuations: The ruble’s volatility against major currencies impacts investor confidence.
- Widespread poverty: Large segments of the population face economic hardships, contradicting growth narratives.
These elements suggest that the growth statistics touted by the Kremlin may be more of a mirage than a reflection of genuine economic vigor. Even as official narratives boast of resilience, the shadows of systemic weaknesses loom large.

Structural Weaknesses: The Hidden Flaws in Russias Economic Model
The façade of a robust economy often disguises underlying vulnerabilities that can threaten its stability. In Russia’s case, several systemic issues lie beneath the surface, quietly undermining the perception of strength. Dependency on energy exports is perhaps the most glaring flaw; with over 60% of its federal budget reliant on oil and gas revenues, fluctuations in global energy prices can wreak havoc on national finances. Moreover, the absence of diversification in various sectors, such as technology and agriculture, further exacerbates this vulnerability, leaving the economy exposed to external shocks and shifting market dynamics.
Additionally, the lack of innovation and investment in productive industries stagnates growth potential. An overwhelming focus on state-owned enterprises often stymies competition and entrepreneurship, leading to a system rife with inefficiencies. Furthermore, an aging demographic presents challenges for the labor market, as a declining workforce struggles to meet the demands of modern industry. These factors coalesce to portray an economic model that, instead of fostering resilience, reveals a precarious alignment that could easily falter under pressure.
| Economic Indicator | Current Status |
|---|---|
| Oil & Gas Revenue | 60% of federal budget |
| GDP Growth Rate | 1.5% (2023) |
| Innovation Index | Unranked in top 40 |
| Demographic Growth | -0.2% annually |

Geopolitical Pressures: How Sanctions Expose Vulnerabilities
Sanctions serve as a testament to the fragility that often lies beneath the facade of a seemingly robust economy. In the case of Russia, the application of economic sanctions by Western nations has revealed weaknesses that were previously obscured by the illusion of strength. The following elements demonstrate how sanctions have unearthed vulnerabilities within Russia’s economic framework:
- Dependency on Energy Exports: A heavy reliance on oil and gas exports has made Russia more susceptible to fluctuations in global energy prices, exposing it to revenue shortfalls during downturns.
- Technological Isolation: Sanctions have curtailed access to critical technology and foreign investment, hampering innovation and modernisation efforts in key industries.
- Inflation and Currency Devaluation: Economic pressures due to sanctions have led to increased inflation and a weakening ruble, impacting the purchasing power of ordinary citizens.
These vulnerabilities are exacerbated by the political and social ripple effects that sanctions can generate. Economic instability often translates into public discontent, which can prompt a narrowing of support for the governing regime. A clear illustration is shown in the table below, demonstrating the impact of specific sanctions on key economic indicators:
| Indicator | Before Sanctions | After Sanctions |
|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth Rate | 3.5% | 0.4% |
| Inflation Rate | 4.1% | 9.9% |
| Rubel Against USD | 60 | 80 |
The data reflects a stark contrast that illustrates how geopolitical pressures have not only exposed economic vulnerabilities but have also precipitated a decline in overall economic health, challenging the narrative of strength that has been prevalent in discussions about Russia’s economic resilience.

Path to Resilience: Strategic Recommendations for Future Economic Stability
To foster a more resilient economic landscape, it is crucial to adopt a multi-faceted strategy that addresses both immediate challenges and long-term sustainability. Key recommendations include:
- Diversification of the Economy: Encouraging investment in non-energy sectors will mitigate over-reliance on oil and gas revenues.
- Innovation and Technology: Boosting support for tech start-ups can drive productivity and enhance competitiveness in global markets.
- Strengthening Trade Relationships: Cultivating ties with emerging economies and diversifying export markets can help insulate the economy from geopolitical shocks.
- Building a Robust Social Safety Net: Expanding social services will provide a cushion during economic downturns and foster public trust.
Equally important is the establishment of sound fiscal policies to ensure sustainable public finances. Implementing transparent governance and curbing corruption will enable more efficient allocation of resources. A concise overview of prioritizing economic resilience can be summarized in the following table:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Diversification | Shifting focus to various sectors beyond energy. |
| Innovation | Incentivizing technology and start-ups. |
| Trade | Expanding partnerships with diverse markets. |
| Governance | Fostering transparency and combating corruption. |
Q&A
Q&A: Unpacking the Illusion of Russia’s Economic Strength
Q1: What prompted the discussion about the actual strength of Russia’s economy?
A1: The dialog around Russia’s economic health has been reignited by a series of geopolitical events, particularly the recent sanctions imposed due to its actions in Ukraine. These developments have led economists and analysts to re-evaluate long-held perceptions of Russia’s economic prowess and challenge the narrative that the country was on a stable, upward trajectory.
Q2: What were some of the indicators that suggested Russia’s economy was stronger than it truly was?
A2: Various factors contributed to the perception of strength, including high oil prices that buoyed state revenues, significant foreign direct investment in energy sectors, and a robust military-industrial complex. Furthermore, macroeconomic metrics like GDP growth rates and foreign reserves often masked underlying vulnerabilities, such as dependency on natural resources and a lack of diversification.
Q3: In what ways did the global economy play a role in shaping the image of Russia’s economic strength?
A3: The global demand for oil and gas created a favorable environment for Russia’s economy, allowing it to project an aura of stability and growth. Additionally, during times of low international energy prices, the Russian government employed various strategies, like currency devaluation and state ownership in critical sectors, which could give the impression of resilience.
Q4: What are the structural weaknesses in Russia’s economy that were often overlooked?
A4: Key structural weaknesses include the heavy reliance on oil and gas exports, which makes the economy vulnerable to price fluctuations. Coupled with a lack of investment in technology and manufacturing, persistent corruption, and underdeveloped infrastructure, these factors indicate that Russia’s economic stability was superficial at best.
Q5: How have recent sanctions affected the perception of Russia’s economic strength?
A5: Sanctions imposed by Western nations have begun to reveal the cracks in Russia’s economic facade. Restrictions on key sectors, particularly finance and technology, have stunted growth and innovation. The immediate effects, such as a decline in foreign investments and a weakened ruble, have forced analysts to reconsider the sustainability of Russia’s pre-sanctions economic narrative.
Q6: Moving forward, what challenges does Russia face in rebuilding its economy?
A6: Russia must confront multiple challenges, including diversifying its economy away from oil dependency, fostering innovation, and reversing brain drain as skilled professionals leave the country. Additionally, recovering from the geopolitical fallout and seeking new trade partnerships outside the West will be crucial for future economic resilience.
Q7: Is there a way for Russia to regain economic stability, or is it too late?
A7: While it may not be too late, regaining stability will require significant systemic changes and a commitment to reform. Fostering domestic entrepreneurship, enhancing infrastructure, improving governance, and re-establishing international trade relations will be essential for a more sustainable economic future.
Q8: What lessons can be drawn from Russia’s experience regarding economic strength and vulnerability?
A8: Russia’s situation serves as a reminder that apparent economic strength can be built on unstable foundations. It highlights the importance of diversification, innovation, and robust institutions as pillars of sustainable economic health, ensuring that nations do not solely rely on external factors such as commodity prices or geopolitical stability.
Key Takeaways
In the intricate tapestry of global economics, Russia’s recent struggles reveal a crucial truth: appearances can be deceiving. Beneath the surface of seemingly robust indicators and displays of strength, a more complex and vulnerable reality has persisted, driven by a confluence of factors including geopolitical tensions, sanctions, and structural inefficiencies. As the nation grapples with shifting tides, the façade of economic might gives way to a landscape marked by uncertainty and adaptation.
The story of Russia’s economy serves as a reminder that strength is not merely measured by numbers and projections, but also by resilience, adaptability, and the ability to navigate unforeseen challenges. As we move forward, it will be essential to keep a watchful eye on the developments within this vast nation, understanding that behind every statistic lies a narrative shaped by history, politics, and the unyielding spirit of its people. The journey ahead will undoubtedly be complex, but in unraveling the fabric of Russia’s economic reality, we gain insights not just into one nation, but into the interconnected world we all inhabit.
ivermectin 6 mg tablet – ivermectin 12 mg oral tegretol 200mg oral
buy accutane cheap – accutane online buy order zyvox 600mg pill
buy amoxicillin medication – buy generic combivent online combivent cheap
order zithromax 250mg online – tindamax 300mg price nebivolol generic
buy omnacortil 20mg online – where can i buy azithromycin prometrium 100mg cost
lasix for sale online – buy furosemide without a prescription betamethasone online buy
clavulanate us – order nizoral 200 mg generic order duloxetine for sale
augmentin ca – nizoral 200 mg ca order cymbalta 20mg sale
order tizanidine pills – tizanidine tablet buy cheap hydrochlorothiazide
order tadalafil 10mg for sale – purchase sildenafil online cheap buy viagra 50mg online
buy sildenafil 100mg for sale – brand tadalafil tadalafil tablet
order cenforce generic – buy chloroquine without a prescription purchase glycomet without prescription
cost lipitor – buy zestril pill lisinopril 2.5mg for sale
where to buy omeprazole without a prescription – pill to stop heart attack atenolol price
how to get depo-medrol without a prescription – pregabalin 75mg over the counter buy generic triamcinolone for sale
desloratadine 5mg brand – priligy ca priligy 30mg canada
brand misoprostol 200mcg – diltiazem for sale online order diltiazem 180mg sale
order acyclovir 800mg pill – generic zovirax 400mg buy rosuvastatin 10mg generic
buy domperidone sale – buy cyclobenzaprine pill cyclobenzaprine pills
buy domperidone for sale – tetracycline 500mg drug order cyclobenzaprine 15mg generic
buy inderal 10mg generic – plavix online order buy methotrexate for sale
I am extremely impressed with your writing skills and also with the structure to your weblog. Is that this a paid topic or did you customize it yourself? Anyway stay up the nice high quality writing, it is uncommon to peer a nice blog like this one today!
buy warfarin 5mg online – buy generic coumadin hyzaar buy online
buy levofloxacin 500mg without prescription – buy levofloxacin cheap purchase zantac online cheap
buy generic nexium over the counter – imitrex 25mg us imitrex 25mg usa
order mobic 15mg generic – purchase tamsulosin generic tamsulosin pill
ondansetron cost – order aldactone 25mg zocor online buy
order valtrex 1000mg for sale – cheap fluconazole 200mg brand diflucan 100mg
Such a useful bit of content.
modafinil pills modafinil 100mg brand provigil oral order modafinil 100mg sale modafinil 200mg generic provigil online order modafinil where to buy
Thanks for putting this up. It’s understandably done.
order azithromycin 250mg for sale – buy tindamax 300mg buy flagyl without prescription
rybelsus 14 mg pill – cheap cyproheptadine 4 mg buy periactin online cheap
motilium medication – motilium cheap buy cyclobenzaprine 15mg pills
order generic inderal 20mg – buy inderal generic methotrexate 5mg tablet
amoxil price – ipratropium 100 mcg generic buy combivent 100 mcg without prescription
buy zithromax 500mg pills – oral bystolic 5mg buy generic nebivolol online
buy clavulanate – atbio info order ampicillin generic
nexium 20mg cheap – anexamate.com nexium 20mg price
buy medex generic – https://coumamide.com/ buy cozaar 25mg without prescription
buy cheap mobic – https://moboxsin.com/ buy generic mobic over the counter